EnviroMail 24 USA
EnviroMail 24 USA - Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs): An Overview
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are persistent organic pollutants widely used in the 1930s-1970s that bioaccumulate in the food chain, reaching high concentrations in animals at the top, such as fish and humans.

What is a polychlorinated biphenyl?
Polychlorinated Biphenyls, or PCB, is a now-banned group of man-made chemicals that were once used in a variety of industries due to their chemical and thermal stability, as well as their high dielectric constant.
PCBs consist of two aromatic rings with different degree of chlorination, ranging from 1 to 10 chlorine atoms. In total there are 209 variations or congeners.
History of PCB and its Subsequent Ban
PCB was first synthesized in 1881 by the German scientists Schmidt and Schultz, and Commercial production started in the early 1920s. They were produced and sold globally for nearly 100 years, with around 700,000 tons produced in the USA, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
PCBs were banned in the United States in 1979, but they are still found in the environment today because of their chemical and physical stability.
PCBs were used in a variety of applications, including:
- Added to insulating fluid for transformer but also to other types of oil (closed applications)
- Used in carbonless copy paper
- Plasticizer in paints
- Additive in flexible PVC coating
- Softener in sealants and coal tar

What are Aroclors?
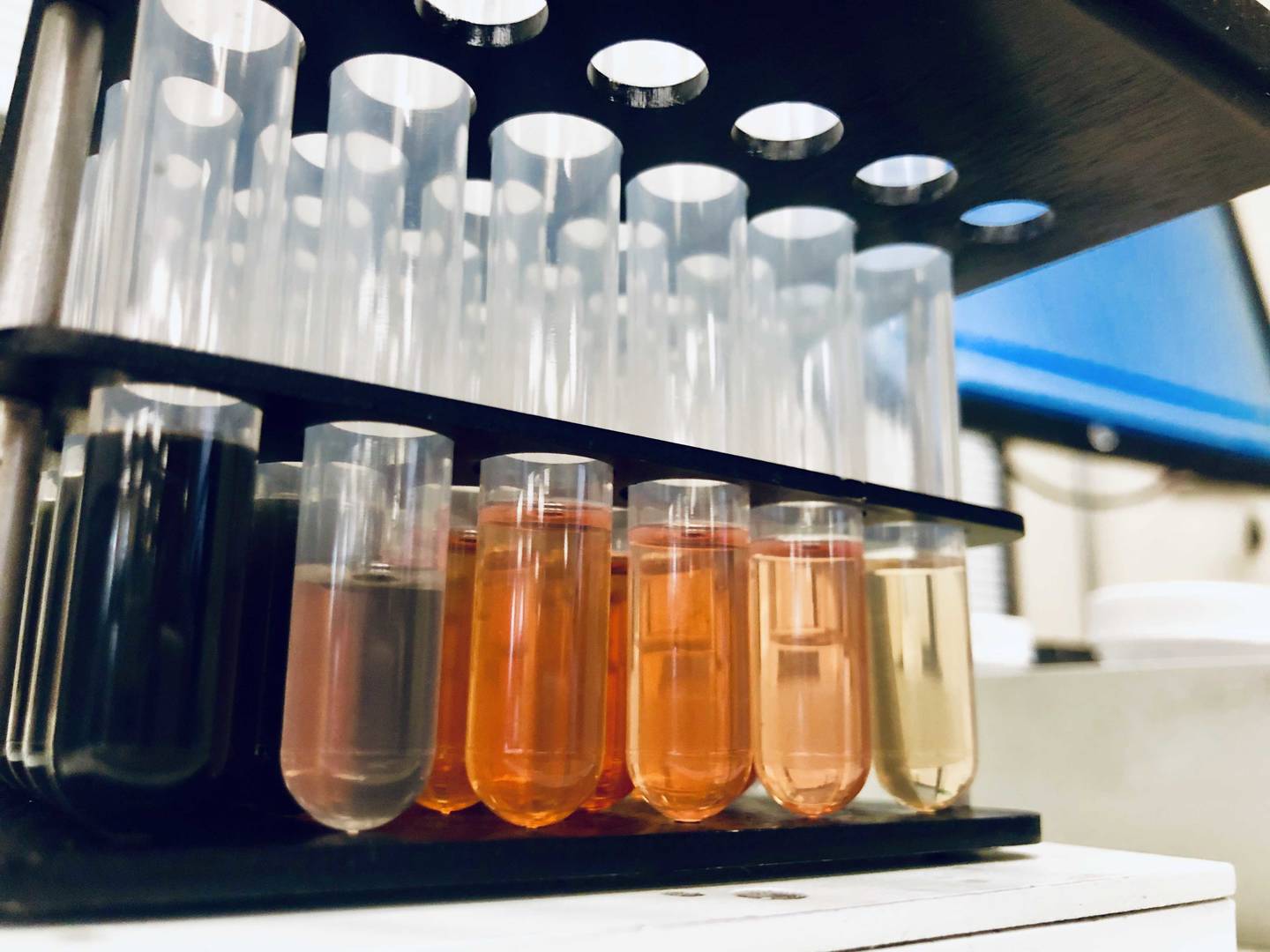
Aroclor was the trade name used for PCB produced and sold in the United States. They were identified by a four-digit code, such as Aroclor 1252. The first two digits indicate the number of carbon atoms in the PCB molecule (12), and the second two digits indicate the percentage of chlorine by weight (52). The exception to this rule is Aroclor 1016.
List of Aroclors2:
| CAS Number | IUPAC Name |
| 12674-11-2 | Aroclor 1016 |
| 147601-87-4 | Aroclor 1210 |
| 151820-27-8 | Aroclor 1216 |
| 11104-28-2 | Aroclor 1221 |
| 37234-40-5 | Aroclor 1231 |
| 11141-16-5 | Aroclor 1232 |
| 71328-89-7 | Aroclor 1240 |
| 53469-21-9 | Aroclor 1242 |
| 12672-29-6 | Aroclor 1248 |
| 165245-51-2 | Aroclor 1250 |
| 89577-78-6 | Aroclor 1252 |
| 11097-69-1 | Aroclor 1254 |
| 11096-82-5 | Aroclor 1260 |
| 37324-23-5 | Aroclor 1262 |
| 11100-14-4 | Aroclor 1268 |
| 12767-79-2 | Aroclor (unspecified) |
Toxicity
All PCB will accumulate in the food chain, as each of its 209 congeners are lipophilic. The toxicity of PCB varies depending on degree of chlorination and structure of the molecule. Some PCBs, often referred to as co-planar PCBs, have similar structure and toxicity to dioxins.
PCB have been demonstrated to cause a variety of adverse health effects including:
- Developmental defects
- Hormonal disruption
- Impaired immune and thyroid function
- Potential cancer
If a company releases PCBs into the environment, they could be held liable for cleanup costs and any damages caused. Testing for PCBs can help companies to identify and remediate PCB contamination before it causes problems.
The United States EPA requires companies to test for PCBs in transformer oil and other electrical equipment.
Analytical Methods for PCB Testing
There are several methods available for PCB analysis, depending on the matrix i.e. soil, water or air, and the legislative requirements. ALS offers the following methods:
Jump to: EPA 508, EPA 608, EPA SW-846 8082, EPA 1668, NIOSH 5503
- EPA Method 508
Method 508 is used for determination of PCB in drinking water. The analysis is performed by a Gas Chromatograph equipped with an Electron Capture Detector, (GC-ECD). The laboratory can report either individual PCB congeners or Aroclors depending on client request.
- EPA method 608
Method 608 is used for determination of PCB in wastewater. The analysis is performed by a Gas Chromatograph equipped with an Electron Capture Detector, (GC-ECD). The laboratory can report either individual PCB congeners or Aroclors depending on client request.
- EPA SW-846 8082
Method 8082 is used for determination of PCB in solid matrices i.e. soil, sediment, solid waste and groundwater. The analysis is performed by a Gas Chromatograph equipped with an Electron Capture Detector, (GC-ECD). The laboratory can report either individual PCB congeners or Aroclors depending on client request.
- EPA method 1668
Method 1668 is used for determining all individual PCB congeners in environmental matrices i.e. Water, Soil, Sediment, Biosolids and Tissue. The analysis is performed by high resolution GC-MS, (HRGC/HRMS).
- NIOSH 5503
Method 5503 is used for determining Aroclors is air after sampling on a sampling train e.g., Florisil tube or Glass Fiber Filter. The analysis is performed by a Gas Chromatograph equipped with an Electron Capture Detector, (GC-ECD).
Protect your business and your community from the dangers of Polychlorinated Biphenyls. Contact ALS today to learn more about our PCB testing services.