Navigating EU Regulation 2023/1545: A Guide for Cosmetics and Personal Care Companies on Fragrance Allergen Labeling
The European Union (EU) has recently updated its regulatory framework concerning the labeling of fragrance allergens in cosmetic and personal care products.

EU Regulation 2023/1545, published 27 July 2023 in the EU Official Journal (OJEU), mandates stricter transparency for consumers regarding potential allergens present in fragrances. ALS helps guide companies through the necessary steps to ensure both compliance and the necessary clinical safety tests that are required to support these efforts.
Regulatory Situation
EU Regulation (EC) 2023/1545, which took effect in 2023, extends the list of fragrance allergens to be labelled in cosmetic products. The Regulation updates Annex III of the EU Cosmetic Products Regulation with 56 new fragrance ingredients for which presence of these allergens should be indicated on the label if their presence exceeds established thresholds for leave on and rinse off products (0.001 and 0.01%).
The EU has provided important deadlines concerning personal care companies. Beauty companies will have to adapt the labels to the new requirements according to the following timelines:
- July 31, 2026: to sell products already on the market or withdraw them from the market.
- July 31, 2028: to place new products that comply with the updated provisions on the EU market.
Potential Allergen List
According to the EU, the new allergens to be indicated on the labels are the following:
- 3-Propylidenephthalide
- Acetyl Cedrene
- Alpha-Terpinene
- Amyl Salicylate
- Anethole
- Benzaldehyde
- Beta-Caryophyllene
- Camphor
- Cananga Odorata Oil/Extract
- Carvone
- Cedrus Atlantica Oil/Extract
- Cinnamomum Cassia Leaf Oil
- Cinnamomum Zeylanicum Bark Oil
- Citrus Aurantium Bergamia Peel Oil
- Citrus Aurantium Flower Oil
- Citrus Aurantium Peel Oil
- Citrus Limon Peel Oil
- Dimethyl Phenethyl Acetate
- Eucalyptus Globulus Oil
- Eugenia Caryophyllus Oil
- Eugenyl Acetate
- Geranyl Acetate
- Hexadecanolactone
- Hexamethylindanopyran
- Isoeugenyl Acetate
- Jasmine Oil/Extract
- Juniperus Virginiana Oil
- Laurus Nobilis Leaf Oil
- Lavandula Oil/Extract
- Lemongrass Oil
- Linalyl Acetate
- Lippia citriodora absolute
- Mentha Piperita Oil
- Mentha Viridis Leaf Oil
- Menthol
- Methyl Salicylate
- Myroxylon Pereirae Oil/Extract
- Narcissus Extract
- Pelargonium Graveolens Flower Oil
- Pinene
- Pinus Mugo
- Pinus Pumila
- Pogostemon Cablin Oil
- Rose Flower Oil / Extract
- Rose Ketones
- Salicylaldehyde
- Santalol
- Santalum Album Oil
- Sclareol
- Terpineol
- Terpinolene
- Tetramethyl acetyloctahydronaphthalenes
- Trimethylbenzenepropanol
- Trimethylcyclopentenyl Methylisopentenol
- Turpentine
- Vanillin
Preparation for Compliance
Understanding the Regulation: EU Regulation 2023/1545 stipulates that any fragrance allergen above EU-specified limits must be listed on the product label. This is to inform consumers who may be allergic or sensitive to specific fragrance compounds.
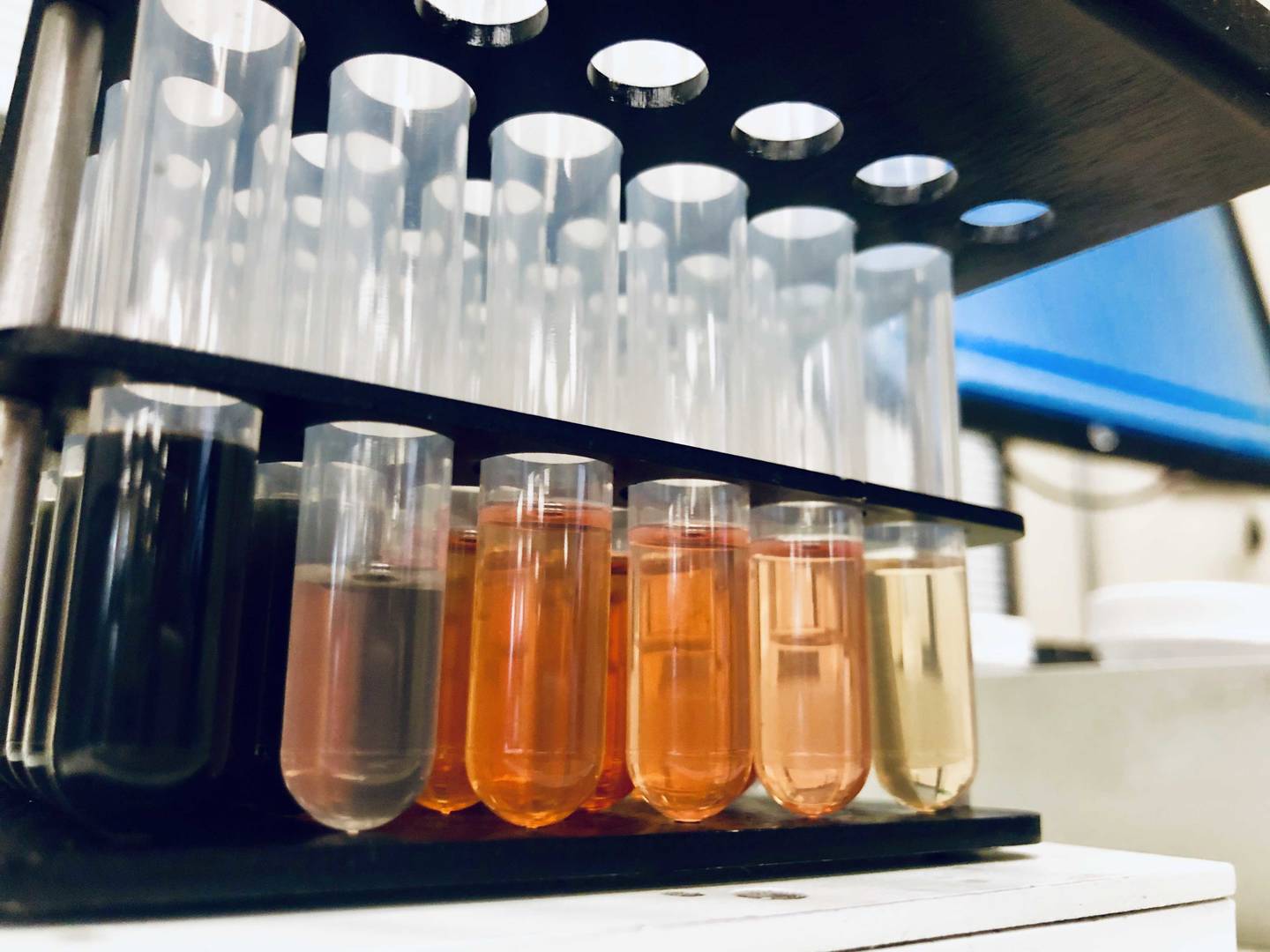
Ingredient Review: Conduct a comprehensive review of all fragrances used in your products. Use a testing laboratory to identify any allergens present and determine if their concentrations fall under the labeling requirements. Testing may include Analytical Chemistry and Safety Studies – HRIPT, Primary Irritation (PI), Cumulative Irritation, Photoallergy, Phototoxicity, Eye Irritation and Safety in Use (SIU) – these clinical tests can be conducted by different medical specialists such as Dermatologist, Pediatricians, Ophthalmologist, Gynecologist and Urologist.
Label Update: Update product labels to include the names of any fragrance allergens that meet or exceed the concentration threshold. Ensure that the labeling is clear, legible, and accessible to consumers.
Staff Training: Educate staff on EU Regulation 2023/1545 to ensure that everyone involved in product development, manufacturing, and quality control is aware of the labeling requirements.
Supply Chain: Work closely with fragrance suppliers to obtain detailed information on the composition of fragrances and ensure that they too comply with the regulation.
Safety Clinical Tests
To support compliance and ensure consumer safety, companies should conduct the following clinical tests:
- Human Repeat Insult Patch Test (RIPT): A more prolonged and repeated exposure test to assess the potential for allergic contact dermatitis from fragrance allergens.
- Phototoxicity and Photoallergy Testing: Since some fragrance allergens can cause reactions when exposed to light, these tests assess the safety of products under UV exposure.
- Analytical Testing: Perform analytical testing to confirm that products are free or below the specification of the new allergens.
- Risk Assessment: A comprehensive risk assessment that considers the cumulative exposure to fragrance allergens from various products used by consumers.
By conducting these tests and closely monitoring the results, companies can not only comply with EU Regulation 2023/1545 but also demonstrate their commitment to consumer safety. It is crucial to work with reputable clinical testing facilities that have experience in regulatory compliance and safety testing for the cosmetics and personal care industry.
EU Regulation 2023/1545 represents a significant step towards greater consumer protection and transparency in the cosmetics and personal care sector. Companies that proactively adapt to these changes and invest in thorough safety testing will be well-positioned to maintain consumer trust and market access within the EU. This draft provides a concise overview of the steps and safety clinical tests required for compliance with the EU Regulation on fragrance allergens labeling. Companies in the cosmetics and personal care industry should take note of these guidelines to ensure they meet the new legislative requirements.
New EU Regulation Annexes and Updates
- 9 Cosmetic Ingredients Published (Includes Vitamin A)
The European Union (EU) Cosmetic Products Regulation 1223/2009 governs the safety and quality standards for cosmetic products within the EU market. However, it does not apply to medicinal products, medical devices, or biocidal products. Recently, an amendment - Commission Regulation (EU) 2024/996 - was introduced, specifically addressing the use of Vitamin A, Alpha-Arbutin, and Arbutin in cosmetic formulations.
This amendment aims to ensure that cosmetic products containing Vitamin A adhere to safe levels. Vitamin A, also known as retinol, is commonly used in skincare products due to its potential benefits for skin health. However, excessive use can lead to adverse effects, such as skin irritation and photosensitivity. Therefore, the regulation sets limits on the concentration of Vitamin A in cosmetic products to safeguard consumers. Cosmetic manufacturers must comply with these regulations when formulating products containing Vitamin A. The EU notified the World Trade Organization (WTO) of this draft regulation in June 2023, emphasizing transparency and international cooperation in cosmetic safety standards.
In summary, the EU's regulatory framework ensures that cosmetic products with Vitamin A meet safety requirements, promoting consumer confidence and protecting public health. Check out the updates.
- Nanomaterials in Cosmetic Products
On March 15, 2024, the European Commission published Regulation (EU) 2024/858, which amends Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 regarding the use of nanomaterials in cosmetic products. This regulation introduces several important changes:
Banned Nanomaterials:
- Styrene/Acrylates Copolymer (nano).
- Copper (nano), Colloidal Copper (nano).
- Colloidal Silver (nano).
- Gold (nano), Colloidal Gold, Gold Thioethylamino Hyaluronic Acid (nano), Acetyl Heptapeptide-9 Colloidal Gold (nano).
- Platinum (nano), Colloidal Platinum (nano), Acetyl Tetrapeptide-17 Colloidal Platinum (nano).
Deadlines:
- The “placing on the market” deadline for these banned nanomaterials is February 1, 2025.
- The “making available on the market” (off-shelf) deadline is November 1, 2025.
Restricted Nanomaterial:
- Hydroxyapatite (nano) is added to Annex III of the EU CPR and is restricted for use under specific conditions.
Hydroxyapatite can be used in toothpaste at a concentration up to 10% and in mouthwashes up to 0.465%. However, it should not be used in applications that may lead to exposure of the end user’s lungs by inhalation.
Criteria for Allowed Nanomaterials:
- Only nanomaterials with specific characteristics are allowed:
- Composed of rod-shaped particles.
- At least 95.8% (in particle number) have an aspect ratio less than 3.
- The remaining 4.2% have an aspect ratio not exceeding 4.9.
- The particles are not coated or surface modified.
Remember to comply with these regulations to ensure the safe use of nanomaterials in cosmetic products. Learn more.
ALS Offers HRIPT Panels on a Weekly Basis
ALS boasts a network of facilities across the USA and Latin America, dedicated to conducting our collaborative HRIPT panels, which enables us to establish a strong and efficient participant recruitment pipeline.
Weekly HRIPT Panels assists customers who are looking to comply with new legislative requirements and consumer safety.
Contact ALS clinical beauty experts: beauty.usa@alsglobal.com or call +1 310 214-0043
Reference sources:
https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32023R1545
https://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/sccs_o_073.pdf
https://cosmeticseurope.eu/files/7516/9893/4117/FINAL_Fragrance_allergens_guide_02_11_2023.pdf
https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=OJ:L_202400996
https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=OJ:L_202400858